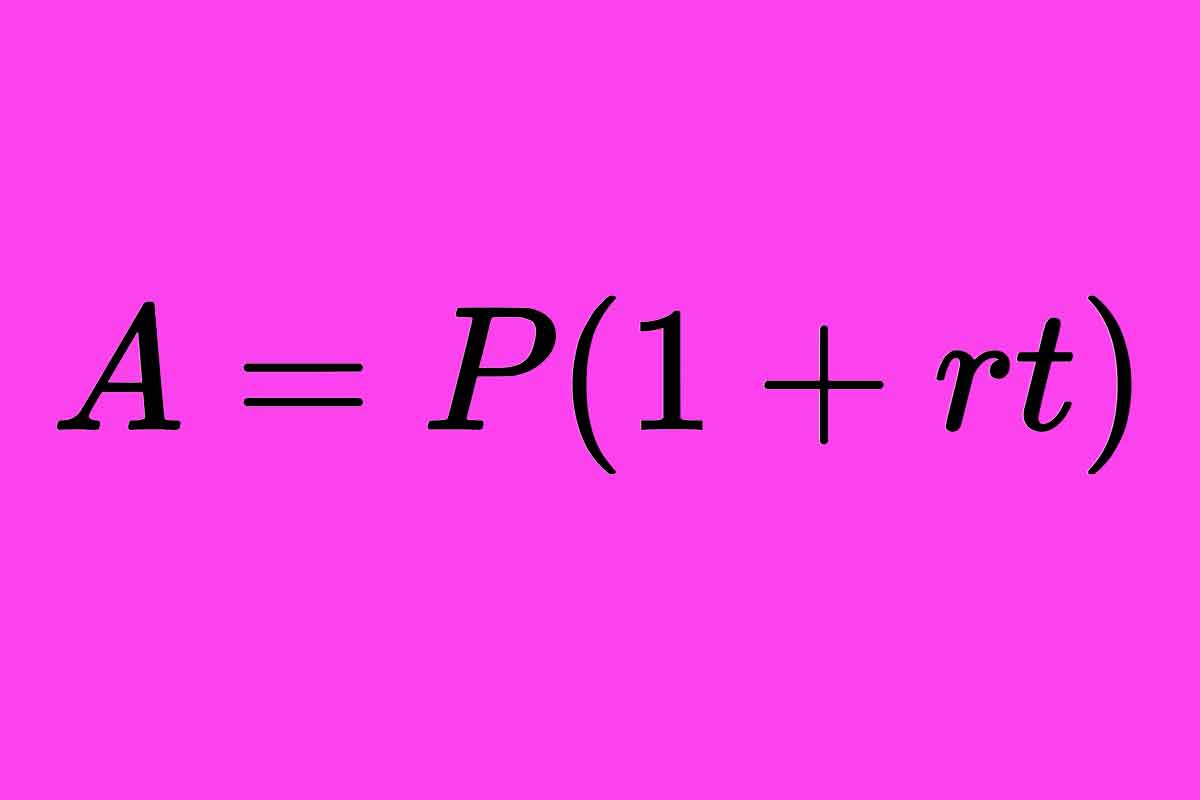When you’re thinking about borrowing money, understanding the concept of interest can seem daunting. But it doesn’t have to be! A simple interest calculator can help you to work out exactly what a loan will cost over time.
What is simple interest in finance?
Simple interest is a type of finance charge that accrues based on the original principal borrowed. It is calculated by multiplying the daily interest rate by the principal, the number of days the money is borrowed and left outstanding.
Featured pro tools
Simple interest does not compound over time, which means it does not increase as more time passes after it has been earned.
When is simple interest used in business?
Simple interest is typically used when the loan or debt obligation is relatively short-term, such as when a company borrows money to purchase inventory.
The amount of simple interest is often quite low and can be paid in one lump sum at the end of the borrowing period. It also works well for loans that have regular payments, such as car loans or home mortgages.
Additionally, simple interest is often used by companies to finance debt obligations with a fixed rate of return. This allows the company to calculate the exact amount of interest due each period, making it easier to budget and plan for repayment.
Simple interest can also be beneficial in other ways. For example, if you are an investor looking for a predictable return, simple interest can help you achieve that.
If you are trying to establish creditworthiness in the eyes of lenders, having a loan with simple interest may be beneficial as it shows your ability to repay debt regularly and on time.
How to calculate simple interest
Simple interest is calculated by multiplying the principal amount, annual interest rate and time period together. The formula for calculating simple interest is:
Interest = Principal x Rate x Time
For example, if you had a loan of £1000 at an annual interest rate of 5% and it was taken out for 1 year, then the interest would be calculated as follows:
Interest = £1000 x 5% x 1 year = £250
Therefore, the total amount payable at the end of the loan period would be £1250.